Head and Neck Cancer Treatment
Contact Us
What are head and neck cancers?
Head and neck cancers refer to a group of cancers that develop in the mouth, throat, voice box (larynx), nose, sinuses or salivary glands. They often begin in the squamous cells that line these moist surfaces. Head and neck cancers are grouped together because they develop in areas of the body that are located close to one another. While they are distinct cancers, they share similar characteristics and risk factors and are often treated in similar ways.
What are the signs and symptoms of head and neck cancers?
Signs and symptoms of head and neck cancers can vary depending on the location, but may include:
- A lump or sore that doesn’t heal
- Persistent sore throat or hoarseness
- Difficulty swallowing
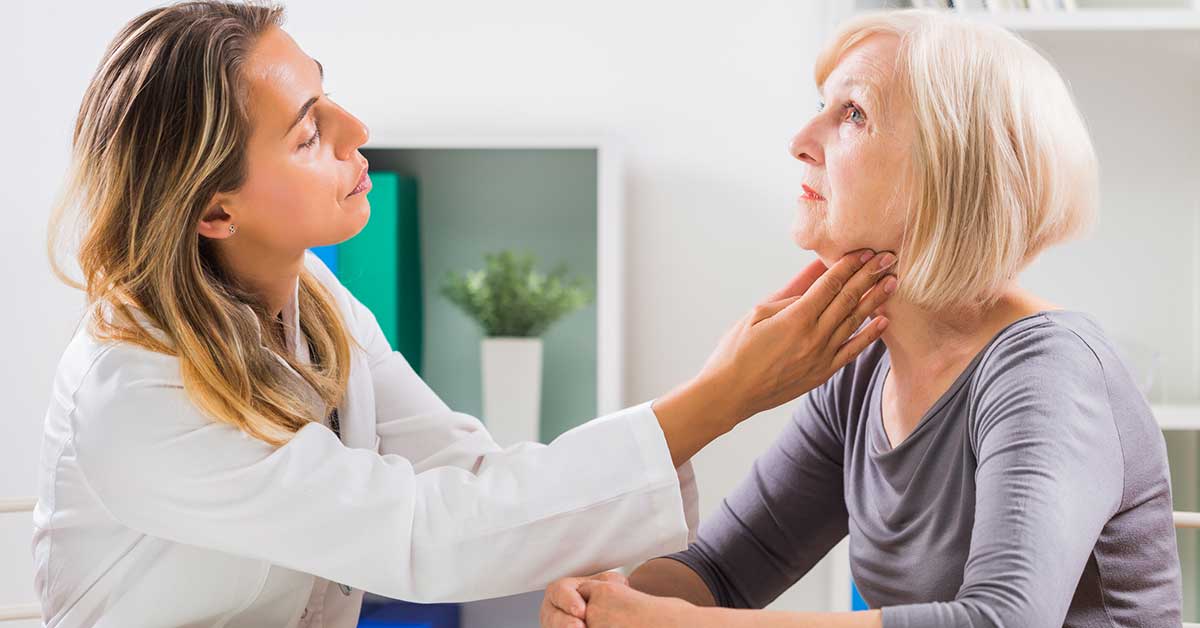
- A lump in the neck
- Ear pain or trouble hearing
- Unexplained weight loss
- Mouth pain or white/red patches in the mouth
- Nasal congestion or nosebleeds (for sinus or nasal cancers)
If symptoms last more than a few weeks or seem concerning, it’s important to see a healthcare provider, as they may signal cancer or another health problem. Taking proactive steps is vital to diagnosing problems early when treatment can be more effective.
How are head and neck cancers diagnosed?
Diagnosing head and neck cancers begins with a review of health history to evaluate the symptoms and a physical exam checking for lumps, swelling or unusual areas in the head, neck and throat. Additional testing to guide diagnosis and treatment planning may include a combination of:
- Imaging tests such as CT, MRI, PET or X-rays
- Endoscopy that uses a thin, flexible tube with a camera to view inside the nose, throat or voice box
- Removal of a small sample of tissue, known as a biopsy, to examine under a microscope for cancer cells
What causes head and neck cancers?
Most cases of head and neck cancers are linked to tobacco and heavy alcohol use, especially when combined. Other causes include:
- Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), linked to certain nasal and salivary gland cancers
- Prolonged sun exposure, which can cause lip or skin cancers
- Exposure to certain chemicals (like asbestos or wood dust)
- Poor oral hygiene
- Poor nutrition
Are head and neck cancers genetic?
Most head and neck cancers are not inherited and are caused by lifestyle factors like tobacco, alcohol and infections. However, in rare cases, genetic factors or inherited conditions (like Fanconi anemia or Li-Fraumeni syndrome) may increase the risk. Genetics may also influence how a person responds to environmental risks. It is best to discuss any potential genetic predisposition with your doctor.
Back to Top
Are head and neck cancers curable?
Yes, head and neck cancers can be curable, especially when found early. The chances of a cure depend on factors like the location, stage and type of cancer, as well as the person’s overall health. Early-stage cancers often respond well to treatment, while advanced cancers may require more aggressive therapy and have a lower chance of cure.
Back to Top
How are head and neck cancers treated?
Treatment options for head and neck cancers depend on a number of factors, including the specific type, stage and location of the cancer, possible side effects, and the patient’s overall health and personal preference. Each patient and each cancer is unique. At FCS, physicians develop a personalized treatment plan in partnership with patients. Head and neck cancers are commonly treated using one or more of the following approaches:
- Surgery to remove the tumor
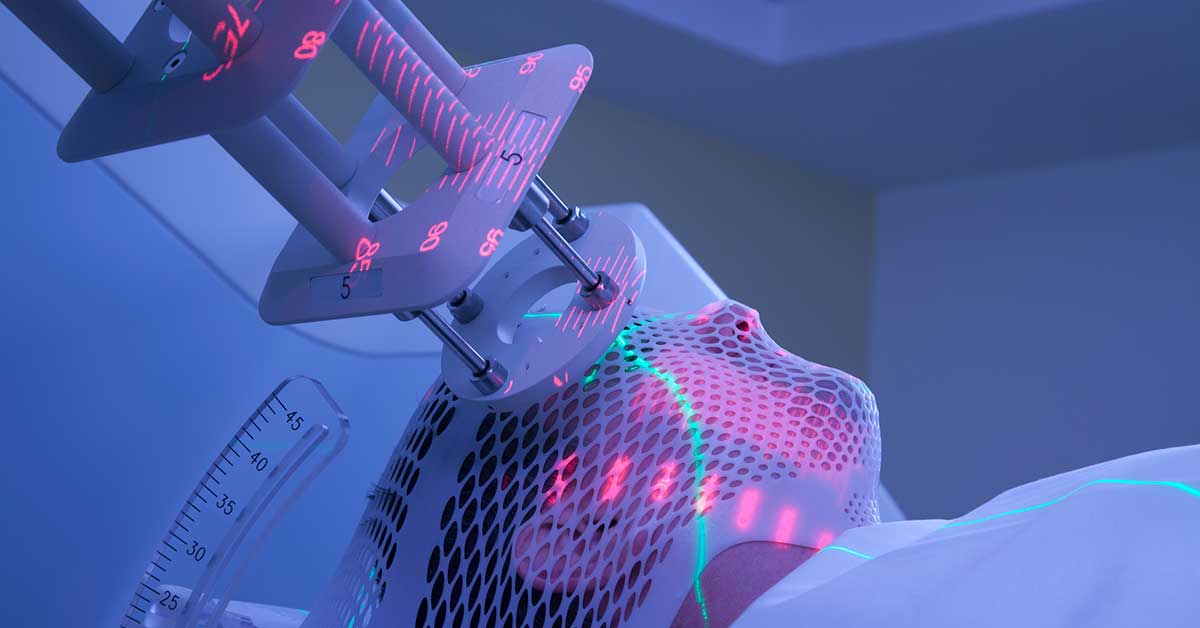
- Radiation therapy to kill cancer cells or shrink tumors
- Chemotherapy using drugs to target cancer cells
- Targeted therapy that attacks specific molecules involved in cancer growth
- Immunotherapy to help the body’s own immune system recognize and attack cancer cells
These treatments may be used alone or in combination. Participation in clinical trials for new therapies or combinations of treatments can be an option, especially for advanced stages of cancer.
Are there screening tests for head and neck cancers?
Currently, there are no routine screening tests widely recommended for head and neck cancers in people without symptoms. However, doctors may perform thorough physical exams and look for signs during regular check-ups, especially in people at higher risk (like heavy smokers). Early detection often relies on noticing symptoms and seeking medical advice promptly.
Back to Top