Oral Cavity (Mouth) and Oropharyngeal (Throat) Cancer
Contact Us
What is oral cavity or throat cancer?
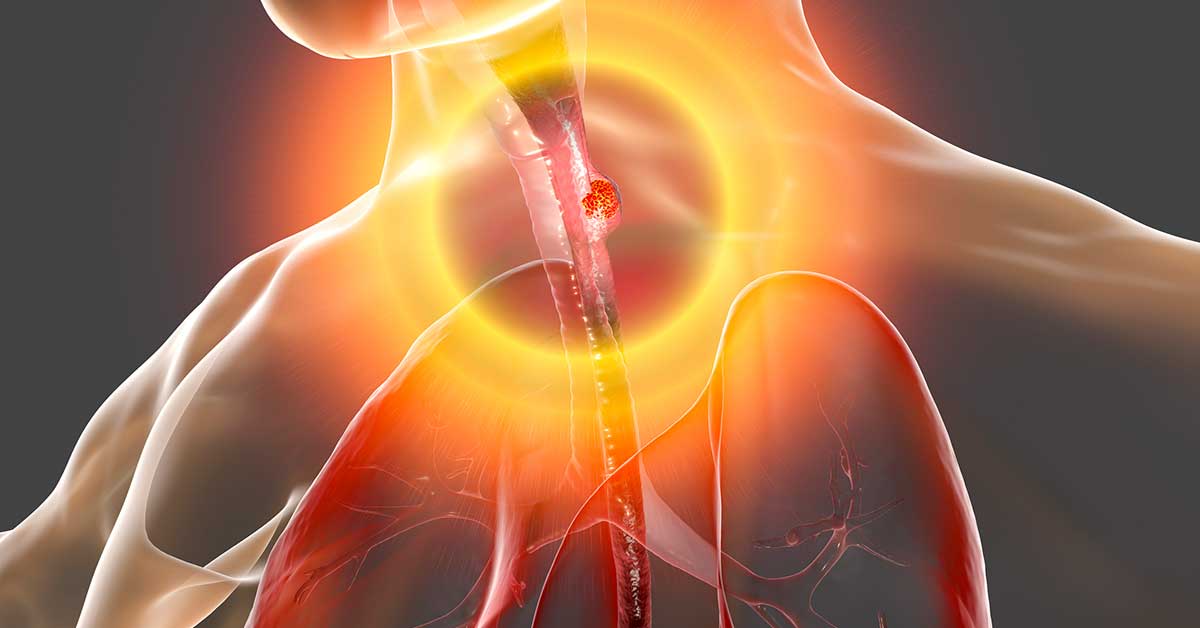
Oral cavity cancer, also called oral cancer, starts in the mouth. Oropharyngeal cancer, or throat cancer, starts in the middle part of the throat. The oral cavity refers to the mouth. It includes the lips, the lining inside the lips and cheeks, the upper and lower gums, the teeth, the front two-thirds of the tongue, the floor of the mouth under the tongue, the bony roof of the mouth (hard palate) and the small area behind the upper and lower wisdom teeth.
The oropharynx is the middle part of the throat just behind the oral cavity that can be seen when your mouth is open wide. It includes the back third of the tongue, the back part of the roof of the mouth (soft palate), the tonsils, and the side and back walls of the throat. The oral cavity and oropharynx help us breathe, talk, eat, chew and swallow. Most oral cavity and throat cancers begin in squamous cells that line moist surfaces, such as those inside the mouth, nose, sinuses and throat. Cancer occurs when these cells develop changes in their DNA and begin to grow out of control.
Other types of oral cavity and throat cancers include:
- Verrucous carcinoma, a rare type of squamous cell cancer most often found in the gums and cheeks.
- Salivary gland cancer that starts in the glands that line the mouth and throat.
- Lymphomas that can start in the tonsils and base of the tongue.
What are the signs and symptoms of oral cavity or throat cancer?
Early warning signs and symptoms of oral cavity or throat cancer can include:
- A sore in the mouth or on the lips that does not heal
- Pain in the mouth that doesn’t go away
- A painless lump or mass in the cheek or on the side of the neck
- A white or red patch on the gums, tongue, tonsil or lining of the mouth
- A sore throat or a feeling that something is caught in the throat that doesn’t go away
- Trouble chewing or swallowing, moving the jaw or tongue
- Numbness of the tongue or other area of the mouth
- Swelling of the jaw that causes dentures to fit poorly or become uncomfortable
- Loosening of the teeth or pain around the teeth or jaw
- Voice changes or hoarseness
- Constant bad breath
Many of these symptoms can also indicate conditions other than cancer. See your dentist or medical doctor right away if any of these symptoms last for more than two weeks.
Back to Top
How is oral cavity or throat cancer diagnosed?
Diagnosing oral cavity or throat cancer begins with a physical examination so that your doctor can evaluate the symptoms you are experiencing. A dentist or medical doctor may use special dyes and/or lights to look for abnormal areas. Additional information to confirm a diagnosis and how advanced the disease is can be obtained through cytology testing or a biopsy to collect tissue samples that are sent to a laboratory for examination to look for any precancerous or cancerous cells. Other types of testing and scans conducted by an ear, nose and throat (ENT) specialist may be necessary to make a definitive diagnosis.
Back to Top
What causes oral cavity or throat cancer?
Most oral cavity cancers are related to tobacco use. This includes cigarettes, cigars, pipes, chewing tobacco and snuff, among others. Heavy alcohol use and excessive sun exposure to your lips can also increase risk. Infection with human papillomavirus (HPV) causes most squamous cell cancers of the throat. HPV is rarely associated with oral cavity cancer and most HPV-positive cancers are diagnosed in young people who have no history of tobacco or alcohol use.
Back to Top
Are oral cavity or throat cancer genetic?
Multiple genetic factors and pathways may contribute to an increase in the risk of head and neck cancer. It is best to talk with your doctor regarding any genetic predisposition to these cancers.
Back to Top
Are oral cavity and throat cancer curable?
When detected early, survival rates for oral cavity and throat cancer increase significantly.
Back to Top
How are oral cavity and throat cancer treated at FCS?
Each patient and each cancer is unique. At FCS, physicians develop a personalized treatment plan in partnership with patients. Treatment options depend on a number of factors, including the specific type and stage of cancer, possible side effects, and the patient’s overall health and personal preference. Surgery is often the first treatment for cancers of the oral cavity and may be followed by radiation and/or chemotherapy. Throat cancers are generally treated with a combination of radiation and chemotherapy. immunotherapies that strengthen and use the body’s own immune system to attack cancer, are yielding positive outcomes as well. Through our extensive FCS clinical trials research program, FCS offers our patients access to the most advanced treatment options available.
Back to Top
What are common risk factors for oral cavity and throat cancer?
Oral cavity and throat cancers account for about four percent of cancers in the U.S. and are diagnosed nearly three times more often in men than in women. About 90 percent of oral cancers occur in people over age 40. However, rates are increasing in younger people, largely due to HPV infection.
Back to Top
Are there screening tests for oral cavity and throat cancers?
There are no routine screening tests for oral cavity and throat cancers. However, these cancers are often discovered during routine dental exams, which is why regular dental and physical checkups are vital. Regular self-examination is also recommended to check for any changes in the mouth, such as patches of discoloration or sores or lumps, although throat cancers can be easily missed. Currently, there is no test to screen for HPV in the throat as there is for cervical cancer.
Back to Top
What does throat cancer look like?
Cancerous tumors are usually quite small and often hidden deep in the throat and throat tissues. Therefore, most patients will not see any visible signs of throat cancer. However, visible signs can include swelling or red or white patches in the throat or visible differences in each side of the throat.
Back to Top
How to check for throat cancer at home?
Regular self-examination is recommended to check for any changes in the mouth or throat, such as patches of discoloration or sores or lumps.
Back to Top
What causes throat cancer?
The use of tobacco or tobacco products is the primary cause of throat cancer. Excessive use of alcohol, a diet lacking in fruit and vegetables and HPV infection also increase the risk.
Back to Top
Is throat cancer treatable?
Throat cancers are generally treated with a combination of radiation and chemotherapy. When detected early, survival rates for oral cavity and throat cancer increase significantly.
Back to Top
What are the signs of throat cancer?
Early warning signs and symptoms of throat cancer can include:
- Pain in the throat or a cough that does not go away
- Coughing up blood
- A feeling that something is caught in the throat that doesn’t go away
- Trouble chewing or swallowing, moving the jaw or tongue
- Shortness of breath
- Voice changes or hoarseness
Can vaping cause throat cancer?
A direct link between vaping and throat cancer has not yet been established. However, vaping is a relatively new smoking alternative, and throat cancer can take years to develop and present symptoms.
Back to Top