Does Aplastic Anemia mean I have Cancer?

What is aplastic anemia?
Aplastic anemia occurs when the bone marrow has difficulty producing the three main types of blood cells: red and white blood cells and platelets. Bone marrow is the soft, spongy tissue found inside your bones where your body makes most of its blood cells.
This leads to:
- Anemia (low red cells): symptoms of fatigue, lack of energy, dizziness, chest pain, shortness of breath or low blood pressure
- Leukopenia (low white cells): symptoms include frequent mild or severe infections
- Thrombocytopenia (low platelets): symptoms include easy or excessive bruising or frequent, heavy bleeding
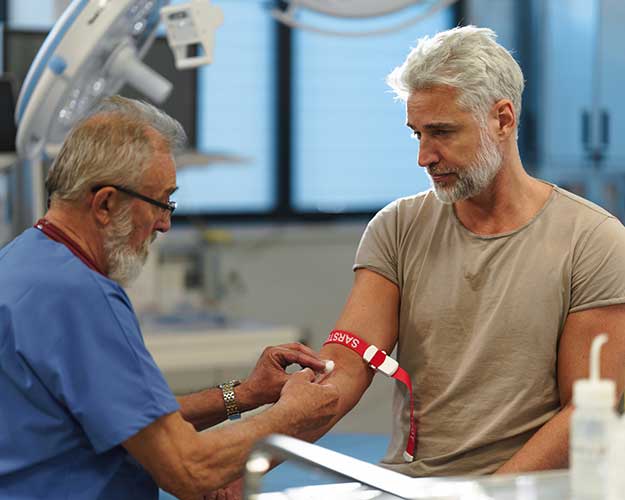
How is aplastic anemia diagnosed?
Aplastic anemia is diagnosed after rigorous blood and image testing to exclude other causes such as infections, blood cancers, autoimmune or nutritional issues. A bone marrow aspirate and biopsy is required to verify the diagnosis.
A bone marrow aspirate and biopsy are tests doctors use to check the inside of your bones to see if the bone marrow is working properly. These are often needed after blood tests are done to confirm a diagnosis.
In a bone marrow aspirate, a small amount of liquid marrow is drawn out with a needle. In a biopsy, a tiny piece of solid bone marrow tissue is taken and reviewed under a microscope.
While blood cancers can behave similarly, aplastic anemia is not considered a cancer. Aplastic anemia can be serious for some individuals, and it is recommended that you see a hematologist, a doctor who specializes in diagnosing and treating blood disorders and diseases, for proper testing and treatment.




Comments