Is Skin Cancer Genetic? Know your Risk
Is Skin Cancer Genetic? Know Your Risk

In the U.S. more people are diagnosed with skin cancer each year than all other cancers combined. Understanding your hereditary risk for skin cancer can be life saving.
What causes skin cancer? There are a variety of factors, including lifestyle, age, genetics, and more. However, there are also things you can do to lower your cancer risk.
In this article you will learn how to identify your skin cancer risk and 5 proactive steps you can take towards early cancer detection.
1. Know Your Family History
Knowing your family history is an important first step in taking a proactive approach to skin cancer prevention. If you have a family member who has been diagnosed with melanoma or other types of skin cancer, you may be at higher risk for developing the disease yourself.
For people with a first-degree relative with melanoma, you have a 50 percent higher chance of developing it than someone without a family history. A first-degree relative includes your biological parents, siblings and children who share about 50% of your DNA. Melanoma prevention isn’t always possible, but knowing you have a family history can help you be on guard and catch it early.
It’s important to talk openly with your relatives about any history of melanoma or other types of skin cancer in the family and to discuss what steps they’ve taken to prevent and manage it. This can help you better understand your own risk factors and make informed decisions about how best to protect yourself.

2. Complete Genetic Screening
Genetic screening is a proactive approach to understanding your risk of developing skin cancer. Through genetic DNA tests, geneticists can identify certain gene mutations that increase your likelihood of developing a wide variety of hereditary cancers.
The most common genes tested for skin cancer are CDKN2A and CDK4, which are linked to familial melanoma. However, there are other genes that may also be tested depending on your family history and other factors.
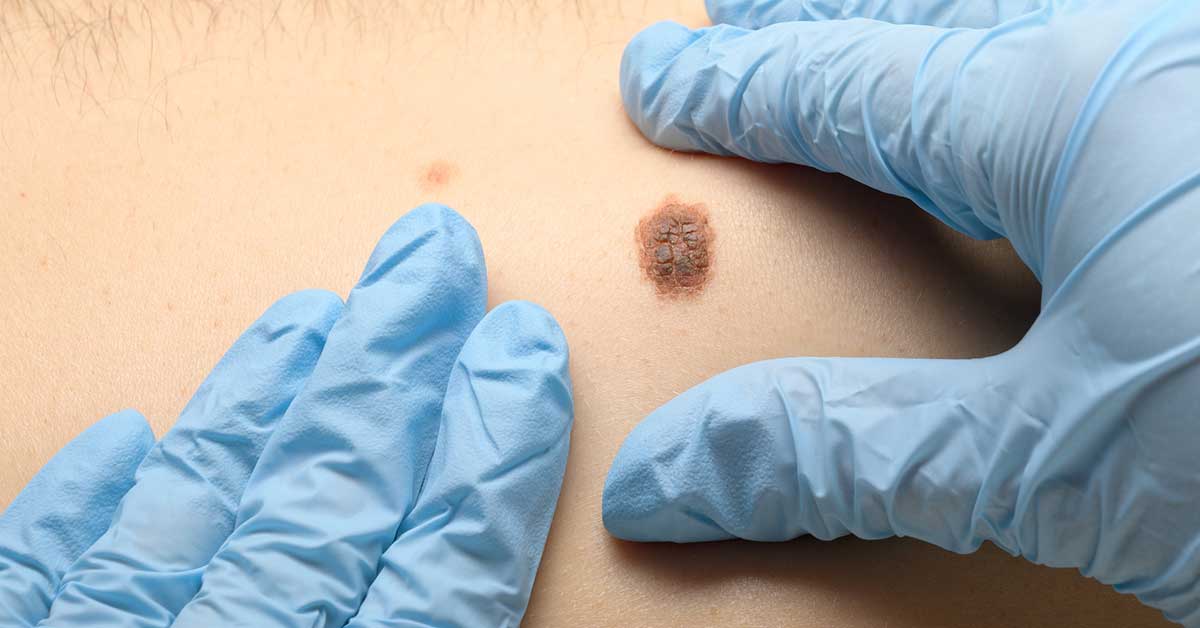
3. Check Skin for Changes
Checking your skin regularly is crucial in catching any potential signs of skin cancer early. Skin cancers can develop anywhere on your body, so it’s important to be thorough when checking for changes.
When examining your skin, use a mirror to check hard-to-see areas like the back of your legs and scalp. Pay attention to any new moles or growths that appear or existing ones that change size, shape, color, or texture. Also, keep an eye out for any sores that don’t heal within two weeks.
It’s recommended to perform self-examinations once a month and take note of anything suspicious to discuss with your doctor. The American Academy of Dermatology offers a step-by-step guide on how to perform a skin self exam.
4. Learn How to Address Common Risk Factors
Understanding the risk factors of skin cancer is crucial in preventing it from happening. Below are a few of the most common risk factors and how to avoid them.
Avoid Harmful Exposure to UV Rays
One major risk factor is prolonged exposure to the sun’s harmful UV rays, which can damage skin cells and increase the chances of developing skin cancer. It’s important to limit time spent in direct sunlight and always wear protective clothing or sunscreen when going outside. Don’t put yourself in a position where you’ve repeatedly abused your skin and increased your risk. Instead of worrying about how to prevent skin cancer after a bad sunburn, be proactive and protect your skin from over exposure. One study found that approximately 86% of melanomas can be attributed to sun exposure. Taking a proactive approach may be life saving.
Fair Skin and a History of Sunburns
Another risk factor is having a history of sunburns, especially during childhood. On average, just one blistering sunburn in childhood more than doubles a person’s chances of developing melanoma later in life. People with fair skin and those with a family history of melanoma are more susceptible to developing skin cancer.
Other Risk Factors
Studies estimate that 1 in 5 Americans will develop skin cancer by the age of 70. By making a plan to reduce methods of exposure that are avoidable, you can help decrease your cancer risk. Other factors that may increase someone’s skin cancer risk include:
- Smoking
- Tanning bed use
- Exposure to certain chemicals or radiation
- Having a weakened immune system due to illness or medication use
To address these risk factors effectively, preventative measures must be taken. Avoid tobacco products and tanning beds completely. Talk to your doctor about your daily routine if you are at risk of exposure to dangerous chemicals or radiation. When reviewing your medical history remember to disclose past and present medications and illnesses, your doctor can help you gain a clear understanding of challenges you may face and changes you can make to decrease your cancer risk.
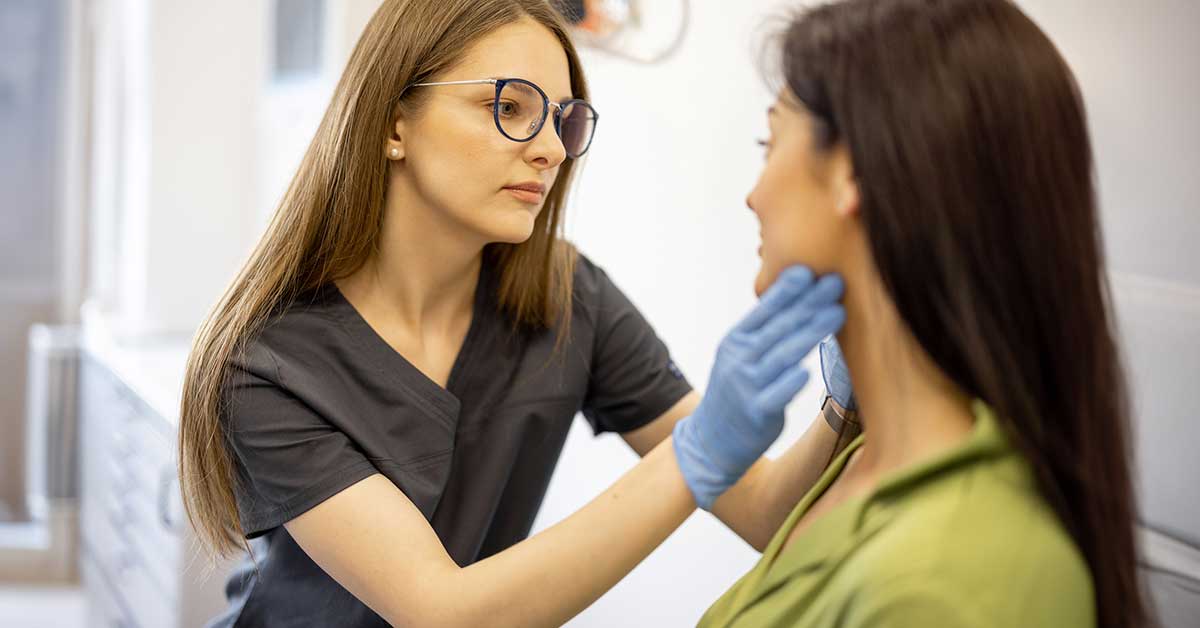
5. Schedule Regular Skin Screenings
It’s important to remember that prevention is not foolproof, and early detection is key. This is why scheduling regular skin screenings with a dermatologist should be an essential part of your overall health plan. A dermatologist can detect any potential warning signs that may have been missed during self-examination and provide prompt treatment if necessary.

What Happens During a Skin Screening?
During the screening, the doctor will carefully examine all areas of your skin to check for any abnormalities or signs of cancerous growths. They may also use a special tool called a dermatoscope to get a closer look at specific spots on the skin. If they find anything suspicious, they may recommend further testing or treatment options.
How Often Should You Have a Skin Screening?
Regular skin screenings are a crucial component of maintaining your health and detecting skin cancer early. The frequency with which you should have a screening depends on multiple factors, including:
- Age
- Family history
- Previous exposure to UV rays
If you’re over the age of 40 or have an increased risk of developing skin cancer due to family history or other factors, it’s recommended that you schedule annual screenings. For those without these risk factors, regular screenings every three years may be sufficient.
Know What Causes Skin Cancer
Knowing what causes skin cancer and proactively taking the steps to reduce your risk can help keep your skin healthy. Additionally, if you’re unsure if you are at high risk for cancer, getting cancer genetic testing can help you form a preventative plan. Don’t leave your health up to chance.
Additional Resources:
- Skin Cancer Facts & Statistics | Skin Cancer Foundation
- Family Matters: What You Should Know About Your Family’s History of Melanoma | Skin Cancer Foundation
- What is a dematoscope, and what does it see? | Medical News Today
- Find Skin Cancer: How to perform a skin self-exam | American Academy of Dermatology Association



Comments