Learn about Bile Duct Cancer - Summary, Symptoms & Treatments
Contact Us
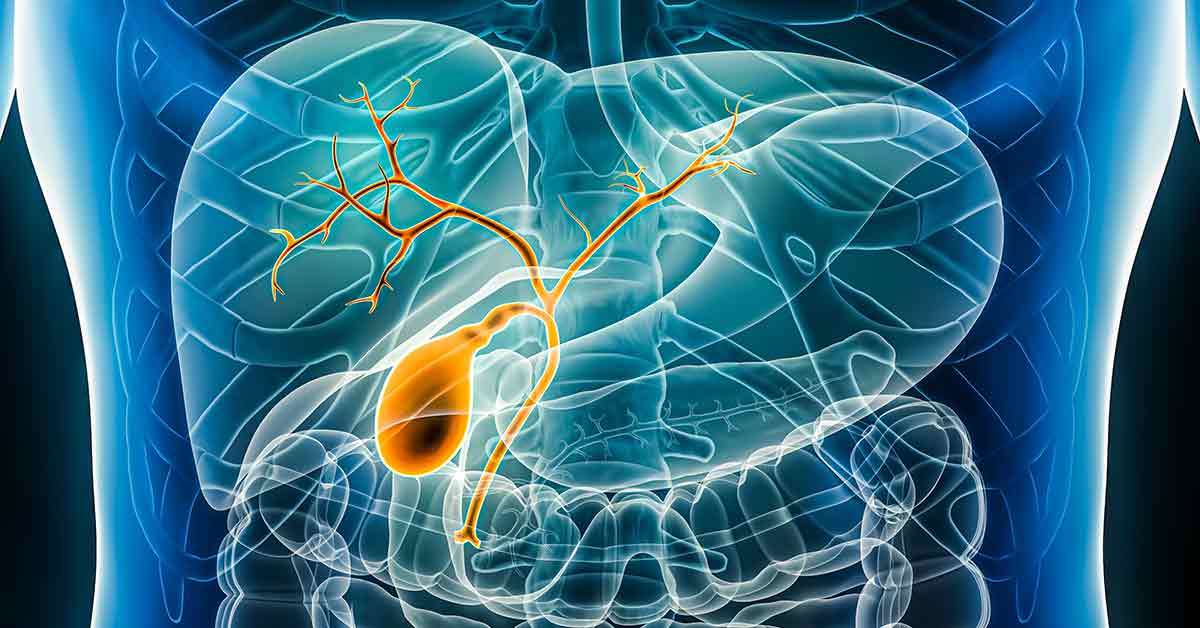
What is bile duct cancer?
Bile duct cancer, also known as cholangiocarcinoma, occurs in the body’s digestive system. Bile ducts are thin tubes that connect the liver and the gallbladder to the small intestine. Bile is a fluid that is made in the liver and stored in the gallbladder. The bile ducts allow bile to go from the liver and gallbladder into the small intestine, where it helps to break down fats into fatty acids, which store energy and provide many other benefits to our bodies.
Bile duct cancer starts when cells in a bile duct begin to grow out of control. Intrahepatic bile duct cancer starts in a part of the bile duct inside the liver. Extrahepatic bile duct cancer stars in a part of the bile duct outside the liver.
What are the signs and symptoms of bile duct cancer?
There are often no signs or symptoms of bile duct cancer, especially in the early stages. When it reaches later stages, warning signs may include:
- Jaundice – yellowing of the skin and the whites of the eyes
- Itchy skin
- Dark-colored urine or pale stools
- Abdominal pain
- Unintended weight loss or loss of appetite
It is important to contact your primary health care provider if you experience any of these on a persistent basis.
Back to Top
How is bile duct cancer diagnosed?
Diagnosing bile duct cancer begins with a physical examination so that your doctor can evaluate the symptoms you are experiencing. Additional information to confirm a diagnosis can be obtained through:
- Lab tests to assess liver function and/or the level of bilirubin in the blood. Bilirubin is the chemical that causes jaundice.
- Imaging tests, such as ultrasound, CT scan or MRI, to look for blockages, abnormalities, or signs of cancer.
What causes bile duct cancer?
The exact cause of bile duct cancer is not known. Researchers have found that the following factors seem to make some people more likely to develop bile duct cancer:
- Inflammation of the liver, due to chronic liver disease, hepatitis or cirrhosis
- Inflammatory bowel disease, such as ulcerative colitis or Crohn’s disease
- Cysts in the bile ducts
- Biliary stones (similar to gallstones, but they form inside the liver)
- Exposure to certain toxins, including asbestos or polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs)
What are common risk factors for bile duct cancer?
The risk of developing bile duct cancer increases with age. The majority of cases occur in adults ages 65 and older. Researchers have found that the following factors seem to make some people more likely to develop bile duct cancer:
- Inflammation of the liver, due to chronic liver disease, hepatitis or cirrhosis
- Inflammatory bowel disease, such as ulcerative colitis or Crohn’s disease
- Cysts in the bile ducts
- Biliary stones (similar to gallstones, but they form inside the liver)
- Exposure to certain toxins, including asbestos or polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs)
Is bile duct cancer genetic?
Gene mutations that are inherited from our parents do increase the risk for some cancers but do not appear to be the cause of bile duct cancer. Most gene mutations that lead to bile duct cancer occur during a person’s lifetime.
Back to Top
Is bile duct cancer curable?
When found early and before the cancer has spread, surgery to completely remove the tumor offers the only chance for a cure. A liver transplant may be an option for some patients.
Back to Top
How is bile duct cancer treated at FCS?
Each patient and each cancer is unique. At FCS, physicians develop a personalized treatment plan in partnership with patients based on the type and stage of the cancer and whether it has spread to other parts of the body. When possible, treatment for bile duct cancer at early stages most often involves surgery. At later stages or if the cancer has spread, treatment may include chemotherapy, radiation or a combination of both to relieve symptoms. Through our extensive clinical trials research program, FCS offers our patients access to the most advanced treatment options available. FCS is at the forefront of developing novel therapies that are proving effective and considered best-in-class treatments for many forms of cancer.
Is there a screening test for bile duct cancer?
There are no screening tests that can reliably detect bile duct cancer.
Back to Top
How fast does bile duct cancer spread?
Bile duct cancer is considered an aggressive cancer. However, the speed at which it spreads varies from person to person.
Back to Top